
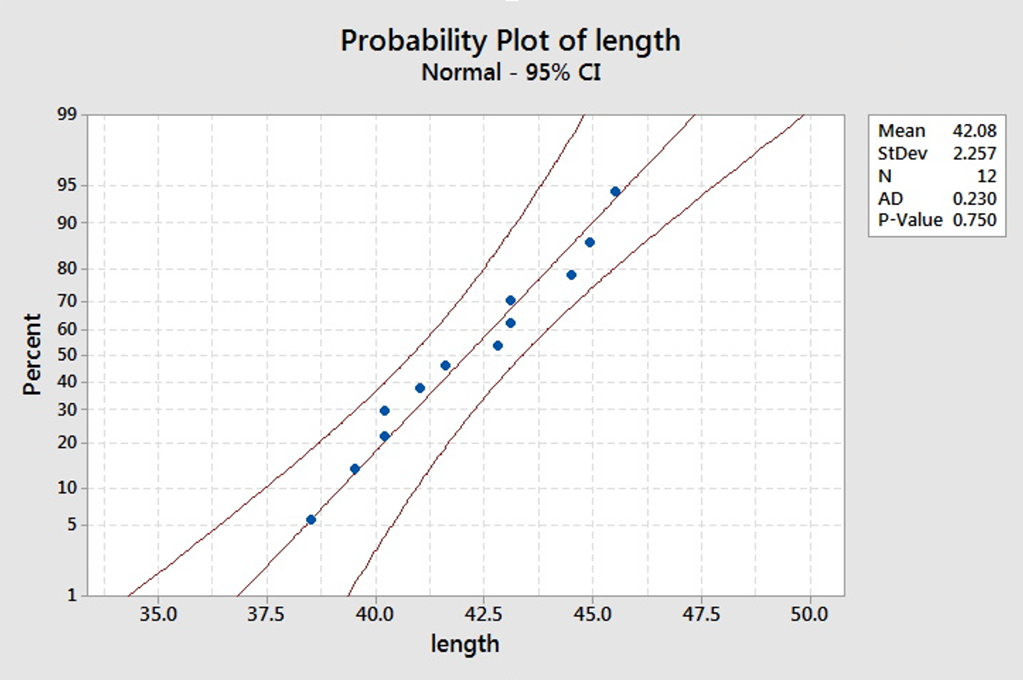
Because the p-value is 0.463, which is greater than the significance level of 0.05, the decision is to fail to reject the null hypothesis. In these results, the null hypothesis states that the data follow a normal distribution.
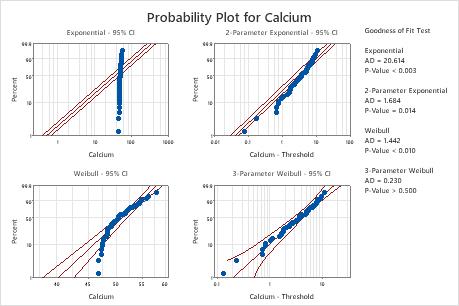
Supplement 2 Median Rank adjustment for SUSPENDED TEST ITEMS. Supplement 1 Further Details of Weibull Probability plotting. D2 Nonparametric Methods for Probability Plotting. You do not have enough evidence to conclude that your data do not follow a normal distribution. D NONPARAMETRIC METHODS AND PROBABILITY PLOTTING. Specifying an arbitrary distribution for your probability scale. Placing your probability scale either axis. They are: Creating percentile, quantile, or probability plots. P-value > α: You cannot conclude that the data do not follow a normal distribution (Fail to reject H 0) If the p-value is larger than the significance level, the decision is to fail to reject the null hypothesis. A closer look at probability plots Overview The probscale.probplot function let’s you do a couple of things. P-value ≤ α: The data do not follow a normal distribution (Reject H 0) If the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level, the decision is to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that your data do not follow a normal distribution. A significance level of 0.05 indicates a 5% risk of concluding that the data do not follow a normal distribution when the data do follow a normal distribution. Usually, a significance level (denoted as α or alpha) of 0.05 works well. A probability plot displays each value versus the percentage of values in the sample that are less than or equal to it, along a fitted distribution line. To create a QQ-plot (quantile-quantile or normal probability plot), select Graph > Probability Plot, choose Simple, and move Price into the Graph. To determine whether the data do not follow a normal distribution, compare the p-value to the significance level. See normal probability plots normal probabilities, calculating in MINITAB, 3536 normal probability distribution, 26, cumulative, 28 probability density.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
